- 15
Sep - 2019MicroPython
6 min | 85122Table of contentShowLast year, I bought an ESP32-CAM board from Banggood and I wanted to use it with MicroPython. The board has an OV2640 without any chip (buffer) between the ESP32 and the camera. There are many implementation for Arduino or directly using Espressif, but I wanted to use MicroPython. Thus, the only solution was to use the I2S interface, but I didn't have time to write the driver. Thus, I put the project on hold. However, last week I was searching between the ESP32 boards that I have, I found the board again, and I also found that tsaarni has written the driver for MicroPython.
This tutorial is about compiling and deploying a version of MicroPython with support for I2S on the ESP32-CAM. Additionally, I included a project with a webserver to take and see the photo. Moreover, I uploaded the compiled firmware, so that you can directly deploy MicroPython with camara support on the board and take photos. The repository of tsaarni has a wiki with instructions, but some steps are not easily to understand and I had some issues with them. Thus, I write the steps again and added more information in this article.
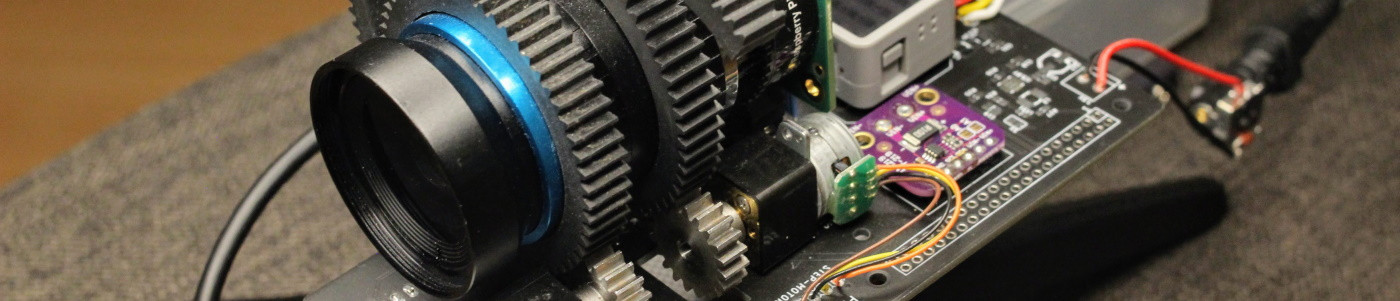
![esp32-cam.jpeg]()
Fig. 1: Photo taken with the ESP32-CAM running MicroPython Hardware & Software
In the following table, you find the hardware and software that you will use for this tutorial:
There are two new articles about this topic:Check out those, before you keep reading this article and instructions.DIY
I uploaded the compiled firmware into the following repository: lemariva/uPyCam. You can deploy the firmware typing the following on a terminal:
esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --baud 460800 write_flash -z 0x1000 esp32-cam-micropython.binHowever, if you want to, you can compile MicroPython yourself. To start with this, you need the following dependencies on your development machine:
# linux sudo apt-get install python3-pip pip3 install virtualenvOn Windows, follow this article to install
pipand installvirtualenvwithpip install virtualenv.Then, put everything you need inside a folder:
mkdir micropython cd micropython export MICROPYTHON=$PWDand start a
virtualenvinside that folder to install the dependencies:# linux . venv/bin/activate # windows myenv\Scripts\activate pip3 install pyserial pyparsingIf you want to, you can also installpyserialandpyparsingas an user or root package. Then, you don't need to install or activate any virtual environment. Just installpython3-pipand then the packages usingpip3 install pyserial pyparsing.Espressif IoT Development Framework (ESP-IDF)
To compile MicroPython for the ESP32-CAM, you need to setup the Espressif IoT Development Framework (ESP-IDF). This can be done typing the following:
cd $MICROPYTHON git clone https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git git checkout <current supported ESP-IDF commit hash> git submodule update --initYou need to look for the right commit hash that is compatible with the current MicroPython version. To do that, look for the Makefile in the MicroPython repository. This is now located here:
micropython-with-esp32-cam/ports/esp32/Makefile. At the moment of writing this article, the supported hash is the following:# the git hash of the currently supported ESP IDF version ESPIDF_SUPHASH := 5c88c5996dbde6208e3bec05abc21ff6cd822d26Or go to the folder
micropython-with-esp32-cam/ports/esp32and typemakewithout having a configured ESP-IDF, you'll get something like:Use make V=1 or set BUILD_VERBOSE in your environment to increase build verbosity. ** WARNING ** The git hash of ESP IDF does not match the supported version The build may complete and the firmware may work but it is not guaranteed ESP IDF path: /home/riva/esp/esp-idf Current git hash: 3eecd43b31a765aae0231ff9a227786bac31b9a2 Supported git hash: 5c88c5996dbde6208e3bec05abc21ff6cd822d26Thus, the above
git checkoutline changes to:git checkout 5c88c5996dbde6208e3bec05abc21ff6cd822d26.Some other requirements are needed depending on your OS. Check the prerequisites to install them.
Then, type the following on a Terminal:
export ESPIDF=$MICROPYTHON/esp-idfToolchain
You can download the toolchain from here: Compiled Toolchain. They are legacy files but they still work. Or you can compile the toolchain with the following (Linux - requirements):
cd $MICROPYTHON git clone https://github.com/espressif/crosstool-NG.git cd crosstool-NG git checkout esp32-2019r1 ./bootstrap && ./configure --enable-local ./ct-ng xtensa-esp32-elf ./ct-ng build chmod -R u+w builds/xtensa-esp32-elfOn Windows, you can download a precompiled toolchain here. MacOS has another requirements.
Then, on Linux/MacOS add the toolchain bin files to the environmental
PATHvariable as:export PATH=$PATH:$MICROPYTHON/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32-elf/binIf you've downloaded it, then extract the files and point the$PATHto the correctbinfolder.OV2640 drivers
You need to add the OV2640 camera drivers to the ESP-IDF. To do that, just type the following:
cd $MICROPYTHON/esp-idf/components git clone https://github.com/tsaarni/esp32-camera-for-micropython.git esp32-cameraMicroPython for ESP32-CAM
After adding the OV2640 drivers to the ESP-IDF, clone the MicroPython version that supports the camera and compile it using the following lines:
cd $MICROPYTHON git clone https://github.com/tsaarni/micropython-with-esp32-cam.git micropython cd micropython/mpy-cross make cd ../ports/esp32 git submodule update --init make V=1 SDKCONFIG=boards/sdkconfig.esp32cam -jFlash MicroPython on the board
The ESP32-CAM does not have a CP2102 to connect it directly to an USB port. Thus, you need an USB to serial device to flash or program the chip.
Connect the USB UART to the ESP32-CAM as described in the following table:
USB UART ESP32-CAM TX U0R RX U0T DTR IO0 5V 5V GND GND If you don't have the DTR pin available (like my board), you need to connect the
GPIO0pin toGNDin order to flash MicroPython firmware. For flashing MicroPython programs, you don't need to do this. Just leave the pin floating. Therefore, after flashing the firmware remove that cable!Then, connect the USB to a free USB port on your PC and type the following:
cd $MICROPYTHON/micropython/ports/esp32 make deployThis last command build the firmware under
build/firmware.binand upload it to the board. After getting these lines:[...] Hash of data verified. Leaving... Hard resetting via RTS pin...disconnect the
IO0pin fromGNDand reset the board using the button.Programming using MicroPython
Read the following article to connect to the board using VSCode: #MicroPython: VSCode IntelliSense, Autocompletion & Linting capabilities.
Use the following code to connect (replace the
ssid_wp2_passwith the right ones) the ESP-CAM to your Wi-Fi router:import network ssid_ = <wlan-ssid> wp2_pass = <wlan-password> sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) sta_if.active(True) sta_if.connect(ssid_, wp2_pass)Then, install the following MicroPython packages typing this lines on the terminal inside VSCode:
import upip upip.install('picoweb') upip.install('micropython-ulogging') upip.install('ujson')Then, clone the MicroPython project located in: uPyCam on your PC configure the
boot.pyfile with the SSID and WPA2 password of the Wi-Fi and upload the files to your board. This project takes a photo with the camera and display it on your browser each time that you visit the webserver that is running on the board.Conclusions
This tutorial is about compiling a MicroPython version with support for the OV2640 camera. The firmware can be uploaded to the ESP32-CAM board to take photos. The resolution of the camera is not ideal, but the low power consumption of the ESP32 and the connectivity make the ESP32-CAM ideal for security and remote applications where the only source of energy is a battery. Furthermore, MicroPython, as usual, makes it easy to develop and update the application. Obviously, some ESP32 performance is lost, but the result is still acceptable.
Thanks Matt for the mention, I really enjoy your recap: October 2019 Melbourne MicroPython Meetup - News Roundup
Tip and Errors
If you get the following error when building the toolchain (
./ct-ng build):Build failed in step 'Extracting and patching toolchain components'. Scroll up and check, which file is giving you the error. In my case, I got the following:[EXTRA] Extracting gcc-git-20df92b4 [00:29] - bzip2: Compressed file ends unexpectedly; [...]Then, remove that file using the following:
cd crosstool-NG/.build/tarballs rm gcc-git-20df92b4.tar.bz2and execute again the builder.
The following error appears because the board is running the official firmware and the version of uasyncio on PyPi is not compatible.
INFO:picoweb:30.000 <HTTPRequest object at 3ffc3590> <StreamWriter <socket>> "GET /" Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "<string>", line 903, in <module> File "/lib/picoweb/__init__.py", line 298, in run File "/lib/uasyncio/core.py", line 161, in run_forever File "/lib/uasyncio/core.py", line 136, in run_forever File "/lib/uasyncio/__init__.py", line 60, in remove_writer TypeError: function takes 2 positional arguments but 3 were givenYou need to replace
__init__.pyandcore.pyin thelib/uasynciodirectory with those from the officialmicropython-lib. I included these files inside the repository. If you upload the complete repository, the files will be replace and you shouldn't get this error.
We use cookies to improve our services. Read more about how we use cookies and how you can refuse them.








Empty